This is a work in progress Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) application, based on the source-filter model of speech:
- Source (Excitation): Raw sound energy. Voiced sounds (vowels) use a periodic buzz (vocal cords); unvoiced sounds (consonants) use noisy airflow.
- Filter (Vocal Tract): Shapes the source sound via throat/mouth/nasal passages, creating resonances (formants) that distinguish sounds (e.g., ‘ee’ vs. ‘oo’).
It analyses input audio to estimate these components and then synthesises the sound from these estimates.
The application processes WAV files in two stages:
Analysis Stage:
Input audio is divided into short, overlapping frames. For each frame, the application estimates:
- Voicing: Whether the frame is voiced (vocal cord vibration) or unvoiced (noise).
- Pitch (if voiced): The fundamental frequency of vibration.
- Filter Characteristics (LPC Coefficients): Vocal tract resonance properties, described by LPC coefficients.
- Gain (Energy): Loudness of the source signal.
Synthesis Stage:
To synthesise the sound, the process is reversed frame by frame:
- Generate Excitation: Creates a pulse train (voiced, at detected pitch) or noise (unvoiced, white/pink).
- Apply Gain: Adjusts excitation loudness using the analysed gain value.
- Filter the Excitation: Shapes the scaled excitation using a digital filter configured with the analysed LPC coefficients, mimicking the vocal tract.
- Combine Frames: Overlaps and adds synthesised frames to create the final waveform.
The result ideally mimics the original sound’s perception using only the extracted LPC parameters.
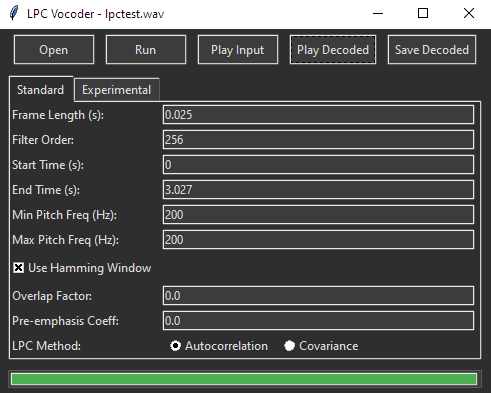
Available controls:
- Frame Length: Analysis segment duration (shorter = faster changes, less frequency detail; longer = opposite).
- Filter Order: Number of LPC coefficients (higher = more spectral detail, more computation).
- Time Selection: Analyse only a specific part of the file.
- Pitch Detection Range: Narrows focus for expected voice frequencies.
- Overlap Factor: Controls frame overlap for analysis/synthesis smoothness.
- LPC Method: Choice of calculation algorithm (e.g., Autocorrelation, Covariance).
- Experimental Settings: Adjust overall gain, noise floor, coefficient shifting, unvoiced noise type, variable frame length.
tags: applications, - LPC